

- #Git add remote and init install
- #Git add remote and init code
- #Git add remote and init download
- #Git add remote and init windows
This adds the file contents to the Index before you commit it. In the Projects window, right-click the file you want to add. Skip adding new or modified files to the Index and commit the required files directly to the HEADġ. Workflow DescriptionĮxplicitly add new or modified files to the Index and then commit only those that are staged in the Index to the HEAD The IDE allows you to choose between the two workflows described in the following table. After you perform the commit, the IDE saves those snapshots in the HEAD. To push local changes and create merge requests.When adding files to a Git repository, the IDE composes and saves snapshots of your project first in the Index. You can now use the upstream as a to pull new updatesįrom the original repository, and use the origin It is common to call this remote repository the upstream. You must create a link to the remote repository to pullĬhanges from the original repository. To keep the project in sync with the original project, you need to pull from the original repository. To create a copy of a repository in your namespace, you fork it.Ĭhanges made to your copy of the repository are not automatically synchronized with the original. Synchronize changes in a forked repository with the upstream Advanced use of Git through the command lineįor an introduction of more advanced Git techniques, see Git rebase, force-push, and merge conflicts. To create a merge request from a fork to an upstream repository, see theįorking workflow. In GitLab, you typically use a merge request to merge your changes, instead of using the command line. Are collaborating on the project with others, and don’t want your work to get mixed up.Ī new branch is often called feature branch to differentiate from the.
#Git add remote and init code
Want to add code to a project but you’re not sure if it works properly.You’re ready to add your changes to the main codebase, you can merge your branch into You can work in your branch without affecting other branches.
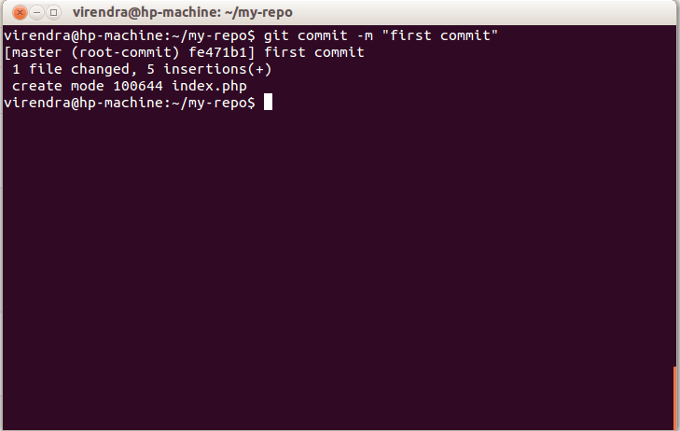
You can learn more on how Git manages remote repositories in theĪ branch is a copy of the files in the repository at the time you create the branch.
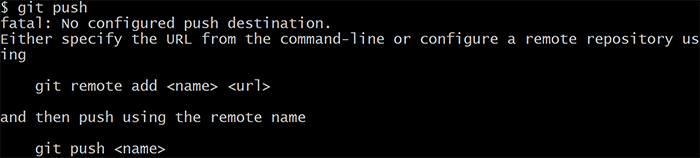
You can create additional named remotes and branches as necessary. is usually the name of yourĮxisting branch. Repository was cloned from, and it indicates the SSH or HTTPS URL of the repository When you clone a repository, REMOTE is typically origin. Git automatically creates a folder with the repository name and downloads the files there.

You can read more on how Git manages configurations in the If you omit -global or use -local, the configuration applies only to the current The -global option tells Git to always use this information for anything you do on your system. You can determine if Git is already installed on your computer by opening a terminal
#Git add remote and init windows
On the Windows taskbar, select the search icon and type cmd. You can integrate it with Zsh and Oh My Zsh for color highlighting and other advanced features. Press ⌘ command + space and type terminal. Prompt, command shell, and command line). To execute Git commands on your computer, you must open a terminal (also known as command
#Git add remote and init install
To help you visualize what you’re doing locally, you can install a
#Git add remote and init download
If you’re new to Git and want to learn by working in your own project,įor a quick reference of Git commands, download a Git Cheat Sheet.įor more information about the advantages of working with Git and GitLab: Like fixing complex merge conflicts or rolling back commits. However, the command line is required for advanced tasks, You can do many Git operations directly in GitLab. Git is an open-source distributed version control system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
